Hotline
+86-136 8495 9862
Email:cennia@szmizhi.com
Add::104,Building 27,Third Industrial Zone, Longxi Community,Longgang District,Shenzhen,China.
Coil Forming & Handling Equipment
Surface Treatment Equipment
Solutions
Application
About Us

Welcome to MIZHI
For consultation/feedback, please call the service hotline: +86-136 8495 9862 Email:cennia@szmizhi.com
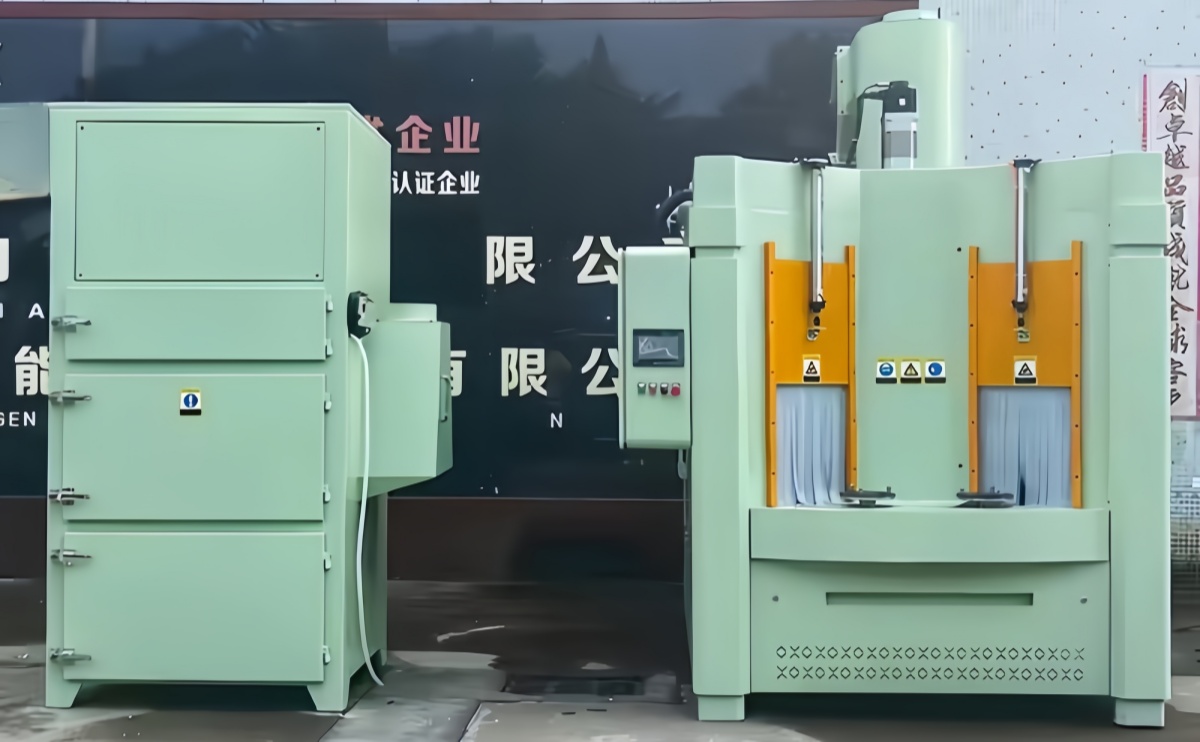
1.Name:Automatic Sandblast
2.Model:MZ
3.Operation Way: Automatic
Introduction to Automated Sandblasting Technology
Automated sandblasting technology represents a significant advancement in surface treatment processes, offering enhanced efficiency, precision, and safety compared to traditional manual methods. This comprehensive guide delves into the working principles, applications, and advantages of automated sandblasting systems.

Working Principle
Automated sandblasting systems operate by combining high-pressure air with abrasive materials to clean and prepare surfaces. The process involves the following steps:
1.Compressed Air Generation:
A compressor generates high-pressure air, which is then regulated to control the pressure and flow. This air is essential for propelling the abrasive material.
2.Abrasive Delivery:
The high-pressure air creates a negative pressure inside the blast gun, drawing abrasive material (such as steel shot, glass beads, or sand) from a storage tank. The abrasive is then propelled through the blast gun.
3.Surface Impact:
The abrasive material is accelerated and ejected from the blast gun, hitting the workpiece surface at high speed. This impact force removes contaminants, rust, paint, and other impurities while increasing surface roughness for better coating adhesion.
4.Material Recovery and Recycling:
After impacting the surface, the abrasive material is collected and separated from waste material. The reusable abrasive is then recycled back into the storage tank for further use.
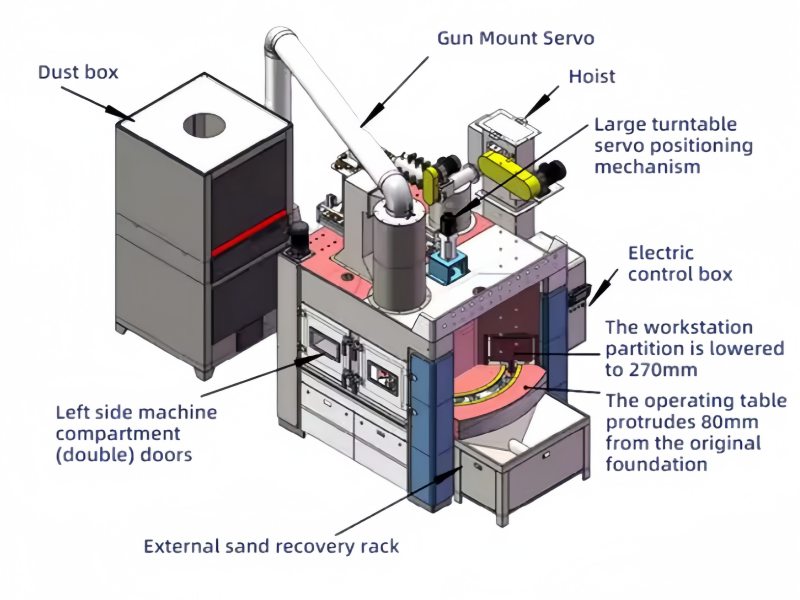
Components of an Automated Sandblasting System
An automated sandblasting system typically consists of the following components:
1.Compressed Air System:
Provides the necessary power for the abrasive delivery. It includes an air compressor, storage tank, filters, and dryers.
2.Abrasive Storage and Feeding System:
Stores and feeds the abrasive material to the blast gun. This system ensures a steady supply of abrasive material.
3.Blast Gun:
The core component that directs the high-speed abrasive stream onto the workpiece. It can be fixed or programmable for different spray patterns.
4.Workpiece Handling System:
Conveys the workpiece through the blasting area, ensuring consistent and uniform treatment. This can include conveyor belts, turntables, or robotic arms.
5.Dust Collection and Filtration System:
Collects and filters dust and debris generated during the blasting process, protecting the environment and operator health.
6.Control System:
Manages the entire process, allowing for precise control over parameters such as pressure, distance, and angle. This system ensures consistent results and high efficiency.
Applications
Automated sandblasting technology is widely used across various industries for its efficiency and precision. Key applications include:
1.Automotive Industry:
Used for removing paint, rust, and other contaminants from metal parts, ensuring surfaces are clean and smooth before painting or coating. For example, engine blocks and cylinder heads are often sandblasted to remove casting residues and oxidation.
2.Aerospace Industry:
Critical for maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) of components. Automated systems provide precise surface preparation, removing oxides and old coatings without damaging the underlying material. For instance, aircraft engine blades require high-precision sandblasting to ensure optimal performance and safety.
3.Manufacturing Industry:
Employed for cleaning molds, dies, and preparing surfaces for welding or bonding. These systems handle large volumes of workpieces with consistent quality, improving throughput and reducing downtime.
4.Construction and Shipbuilding:
Used to prepare concrete surfaces, clean steel structures, and remove coatings from various materials. In shipbuilding, they maintain hull integrity by removing marine growth and old paint.
5.Glass and Stone Processing:
Used for engraving and decoration. By adjusting the type and particle size of abrasives and the pressure and angle of the spray, unique textures and patterns can be created on glass and stone surfaces.
Advantages
1.Improved Safety:
Automated systems reduce worker exposure to hazardous environments, minimizing health risks associated with inhalation of abrasive particles and dust. For example, operators no longer need to wear heavy protective gear, reducing physical strain.
2.Enhanced Precision:
Robotic arms and programmable systems provide precise control over the sandblasting process, ensuring consistent results and reducing the risk of damaging the workpiece. The precision can be as high as 0.1mm, which is unattainable by manual labor.
3.Higher Quality:
Automated systems produce uniform surface finishes, meeting high-quality standards and ensuring better adhesion of coatings. This consistency is crucial for industries like aerospace, where surface quality can affect the performance and safety of components.
4.Increased Productivity:
These systems can operate continuously without breaks, optimizing production processes and reducing lead times. For example, a robotic sandblasting system can work around the clock, significantly increasing output compared to manual labor.
5.Cost Savings:
While the initial investment can be significant, the long-term savings in labor, improved productivity, and reduced material waste make automated sandblasting a worthwhile investment. For instance, a study showed that automated systems can reduce labor costs by up to 70%.
6.Environmental Compliance:
Modern automated sandblasting systems are designed with environmental compliance in mind. They often include dust collection and filtration systems to minimize pollution.
7.Future Trends
The future of automated sandblasting technology looks promising, with advancements in areas such as intelligence, precision, and environmental sustainability. Trends include:
(1) Intelligentize(Intelligent Systems):
Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize sandblasting parameters in real-time, further improving efficiency and quality.
(2) Precision Control:
Enhanced precision in controlling sandblasting parameters to achieve even more uniform and high-quality surface finishes.
(3) Environmental Sustainability:
Development of more environmentally friendly abrasives and processes to reduce the environmental impact of sandblasting.
(4) Cost Reduction:
Continued efforts to reduce operational costs through energy efficiency and optimized abrasive usage.
Automated sandblasting technology represents a significant leap forward in surface treatment processes, offering numerous advantages over traditional methods. Its applications span across various industries, from automotive and aerospace to construction and glass processing. As technology advances, we can expect even greater efficiency, precision, and environmental compliance from automated sandblasting systems.